Why Do I Keep Getting Invalid Syntax in Python?: Troubleshoot Now
You keep getting invalid syntax in Python due to typos, incorrect indentation, or missing punctuation. Verify your code for common mistakes.
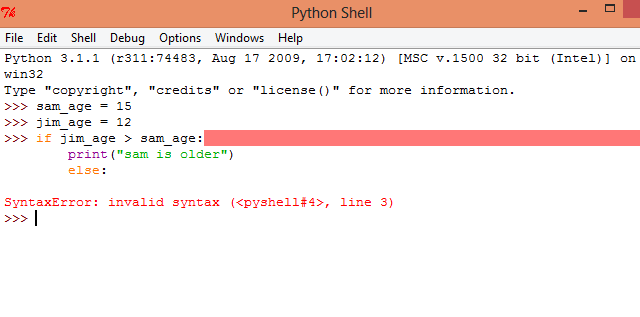
Python’s syntax errors often frustrate new and experienced programmers alike. These errors stem from small, easily overlooked issues like typos or incorrect indentation. A missing colon or misplaced parenthesis can trigger an invalid syntax error. Ensuring your code follows Python’s strict formatting rules is crucial.
Carefully review your code for common pitfalls such as mismatched brackets, missing colons, or improper use of quotes. Utilizing an Integrated Development Environment (IDE) with syntax highlighting can help identify errors. Regularly running and testing your code in smaller sections can also prevent syntax errors from escalating. By being meticulous, you can avoid these frequent mistakes and improve your coding efficiency.
Common Syntax Errors
Python is popular for its simplicity. Yet, many face syntax errors. Understanding common syntax errors can help you code better.
Indentation Issues
Python uses indentation to define code blocks. Incorrect indentation leads to syntax errors.
Here’s an example:
def my_function():
print("Hello World") # This will raise an IndentationError
Correct it by adding proper indentation:
def my_function():
print("Hello World") # This is correct
Always use consistent indentation. Python recommends using four spaces per indentation level.
Mismatched Parentheses
Mismatched parentheses are common. They can occur in function calls, conditionals, or loops.
Example of a mismatched parenthesis:
print("Hello World" # Missing closing parenthesis
Ensure every opening parenthesis has a closing counterpart:
print("Hello World") # This is correct
Use tools like code editors to highlight mismatched parentheses.
| Common Error | Explanation |
|---|---|
| IndentationError | Code is not properly indented. |
| SyntaxError | Parentheses or other symbols are mismatched. |
By understanding and correcting these common errors, you can write cleaner Python code.

Credit: stackoverflow.com
Misuse Of Keywords
Invalid syntax in Python often results from the misuse of keywords. Python keywords are special words that perform specific functions. Misusing these reserved words can lead to syntax errors. Understanding the correct usage is crucial for error-free code.
Reserved Words
Python has a list of reserved words that you cannot use as identifiers. These words have predefined meanings in Python. Using them incorrectly will cause syntax errors.
| Keyword | Function |
|---|---|
| and | Logical AND operator |
| if | Conditional statement |
| for | Looping construct |
| def | Function definition |
Misusing these keywords can disrupt the code flow. Always use them in their intended context.
Incorrect Usage
Incorrect usage of keywords is a common mistake. Let’s look at some examples.
- Using for as a variable name:
for = 5 # This will cause a syntax error - Incorrect use of if:
if 5 # Missing condition and colon - Misusing def:
def = 10 # This is not allowed
Always ensure that you are not using reserved words as variable names or in other incorrect ways. Checking the list of Python keywords can prevent such errors.
String Formatting Mistakes
String formatting mistakes are common in Python. These errors often cause invalid syntax issues. Let’s explore some common mistakes.
Missing Quotes
One of the most frequent errors is missing quotes. Strings in Python must be enclosed in quotes. This can be single (‘), double (“), or triple quotes (”’ or “””).
For example:
print(Hello World)The above code will cause a syntax error. The correct way is:
print("Hello World")Ensure your strings are always enclosed in quotes.
Improper Escape Characters
Improper use of escape characters often leads to syntax errors. Escape characters in Python start with a backslash (\). They allow you to include special characters in strings. Common escape characters include:
- \n for newline
- \t for tab
- \\ for backslash
Consider the following example:
print("This is a backslash: \")This will cause a syntax error. The correct way is:
print("This is a backslash: \\")Always double-check your escape characters.
Credit: realpython.com
Incorrect Variable Names
Many beginners face syntax errors in Python due to incorrect variable names. Understanding the rules for naming variables is crucial. These rules help avoid common mistakes.
Case Sensitivity
Python is case-sensitive. This means that Variable and variable are different. Always pay attention to letter cases. For example:
variable = 10
print(Variable) # This will cause an error
In this example, Variable is not defined. Only variable exists. So, Python will throw an error.
Special Characters
Variable names should not contain special characters. Only letters, numbers, and underscores (_) are allowed. Using other characters can cause syntax errors. For instance:
my-variable = 10 # This will cause an error
my_variable = 10 # This is correct
In the first line, the hyphen (-) is not allowed. In the second line, the underscore (_) is correct.
Common Errors with Special Characters
- Using spaces in variable names
- Starting variable names with numbers
- Including symbols like @, #, $, etc.
| Incorrect | Correct |
|---|---|
| my variable = 10 | my_variable = 10 |
| 2ndVariable = 5 | second_variable = 5 |
| my@variable = 20 | my_variable = 20 |
Follow these rules to avoid syntax errors in Python. Proper variable names make code easier to read and debug.
Function Definition Errors
Function definition errors are common in Python. These errors can cause invalid syntax issues. Understanding these errors helps you write clean code. This section covers two main problems: Missing Colons and Improper Indentation.
Missing Colons
Missing colons are a frequent error in Python. When defining a function, you must use a colon. It indicates the start of the function’s body. Without a colon, Python throws a syntax error.
Example:
def my_function() # Missing colon here
print("Hello, World!")
Corrected Code:
def my_function(): # Colon added
print("Hello, World!")
Improper Indentation
Python relies on indentation to define code blocks. Improper indentation leads to syntax errors. Always use consistent spacing in your code.
Example:
def my_function():
print("Hello, World!") # Improper indentation
Corrected Code:
def my_function():
print("Hello, World!") # Proper indentation
Here’s a table summarizing common function definition errors:
| Error | Example | Fix |
|---|---|---|
| Missing Colon | def my_function() | def my_function(): |
| Improper Indentation | print(“Hello, World!”) | print(“Hello, World!”) |
Always check for missing colons and indentation. These checks prevent common syntax errors.
List And Dictionary Issues
One common error in Python is invalid syntax. This often happens with lists and dictionaries. This section will address these issues. We will focus on incorrect brackets and key-value pairs. These are frequent culprits of syntax errors.
Incorrect Brackets
Lists and dictionaries use different brackets. Lists use [] while dictionaries use {}. Mixing these can cause errors.
For example, a list should look like this:
my_list = [1, 2, 3]A dictionary should look like this:
my_dict = {"key1": "value1", "key2": "value2"}Using the wrong brackets will lead to syntax errors.
Key-value Pairs
In dictionaries, you must use key-value pairs. Each key must have a corresponding value. Forgetting this will cause errors.
Here is the correct way to define a dictionary:
my_dict = {"name": "Alice", "age": 25}Common errors include missing colons or commas. Always check for these in your code.
| Common Error | Example |
|---|---|
| Missing colon | {"name" "Alice"} |
| Missing comma | {"name": "Alice" "age": 25} |
Keep these tips in mind. They will help you avoid syntax errors in your Python code.
Module Import Problems
One common reason for invalid syntax in Python is Module Import Problems. Issues with importing modules can disrupt your code. These problems arise from typographical errors and circular imports.
Typographical Errors
Typographical errors in import statements often lead to invalid syntax. Python is case-sensitive, so ensure you match the exact name of the module.
For instance, importing a module incorrectly:
import NumpyShould be:
import numpyCheck for extra spaces or missing underscores in your module names. These small mistakes can cause big issues in your code.
Circular Imports
Circular imports occur when two or more modules depend on each other. This creates a loop and Python cannot resolve the imports. To avoid this, structure your code wisely.
For example, if module A imports module B, and module B imports module A, you get a circular import.
This circular dependency can be fixed by reorganizing your imports:
- Move imports to a function or method.
- Use import statements within functions to avoid circular dependencies.
Here is an example of resolving circular imports:
# module_a.py
def func_a():
from module_b import func_b
func_b()
# module_b.py
def func_b():
from module_a import func_a
func_a()
By restructuring, you break the circular dependency.
Debugging Tips
Debugging Python syntax errors can be frustrating. But with the right tips, it gets easier. Here are some effective tips to help you.
Read Error Messages
Python gives error messages when it finds invalid syntax. These messages are helpful. They tell you where the problem is. Always read the error messages carefully.
For example, if you see an error like:
SyntaxError: invalid syntax
Check the line number mentioned. Look at that line in your code. Often, the error is just a missing comma or bracket.
Use An Ide
An Integrated Development Environment (IDE) can help you a lot. IDEs highlight syntax errors. They show you exactly where you made a mistake. This saves you time and effort.
Here are some popular Python IDEs:
- PyCharm
- Visual Studio Code
- Spyder
These tools also have features like code completion and debugging. This makes writing Python code much easier.
Using an IDE helps you learn and fix mistakes quickly. It is a great way to improve your coding skills.

Credit: discuss.python.org
Frequently Asked Questions
What Causes Invalid Syntax In Python?
Invalid syntax in Python usually occurs due to typos, missing colons, or unmatched parentheses. Ensuring proper indentation and correct spelling helps avoid these errors.
How Can I Fix Python Syntax Errors?
To fix Python syntax errors, carefully check your code for missing colons, unmatched parentheses, and correct indentation. Use a code editor with syntax highlighting.
Why Does Python Require Indentation?
Python uses indentation to define code blocks. Proper indentation ensures your code is structured correctly and runs as intended.
Can Incorrect Quotes Cause Syntax Errors?
Yes, incorrect or mismatched quotes can cause syntax errors in Python. Ensure you use matching single or double quotes consistently.
Conclusion
Understanding why you get invalid syntax in Python is crucial for smooth coding. Common issues include missing colons, incorrect indentation, or unmatched brackets. By double-checking your syntax and using tools like IDEs, you can avoid these errors. Keep practicing and soon these mistakes will be a thing of the past.
Happy coding!